Business Process Modeling Example - Multiplication of tasks
When modeling business processes, there are often situations when the correct modeling options are either unknown or there are several, and only one of them needs to be selected. In this article we'll look at one process and various versions of its execution and modeling in the BP Simulator service.
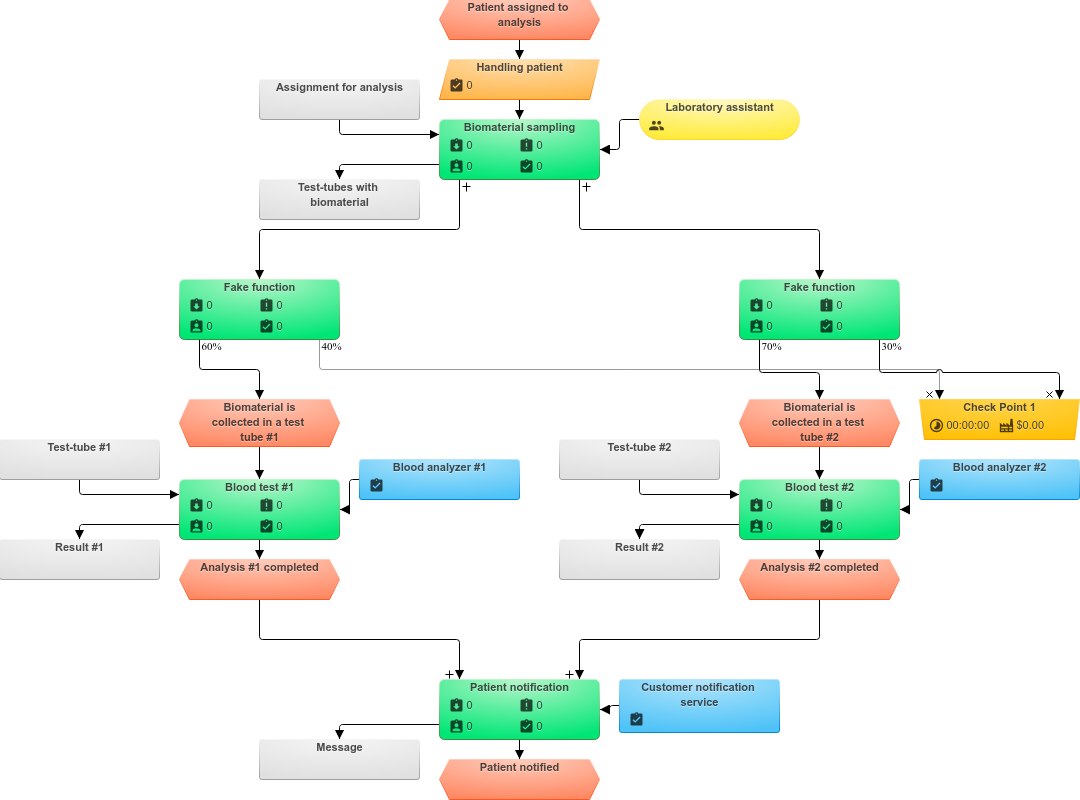
Modeling of the basic procedure for the analysis of biomaterial
As a demonstration process, let's take a simplified procedure for analyzing the biomaterial in a medical laboratory. For the analysis result the patient must give blood, and the Laboratory of conduct its analysis and inform the patient. We simulate this procedure by placing the following objects of the business process model on the model:
- Task Generator "Handling patient" - each client who applies for the analysis forms a task for the laboratory. Pay attention, the patient himself is not the executor of the business process, therefore he is not applied to the model.
- Function "Biomaterial sampling" - the lab technician must take the patient's blood into the test tube.
- Function "Blood test" - placing a sample of biomaterial in the analyzer and conducting the study. Despite the fact that the performer of this and the previous function can be the same, it is impossible to combine these functions, because between them can be the waiting/preparation time of the instrument or the executor may be changed.
- Function "Patient notification" - at the end of the analysis, the laboratory assistant sends the result of the analysis to the patient. For a similar reason, we will not combine this function with the previous one.
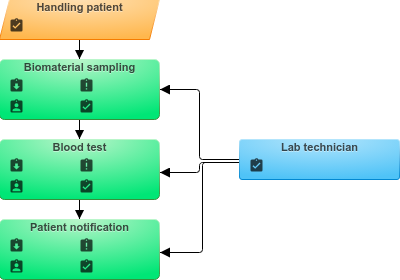
Version #1: 1 client and 2 required parallel tasks
Let's consider the possibility of modeling such cases when the process instance is one (one client launched one process), and there are several parallel tasks to complete the procedure. For example, a patient needs to make two different blood tests. We will not consider the variant with sequential fence and analysis in this article, although this can often be a good variant of modeling, but in this case we add a new condition that affects the duration of the function:
- The Analysis №1 lasts 1 hour
- The Analysis №2 lasts 2 hours
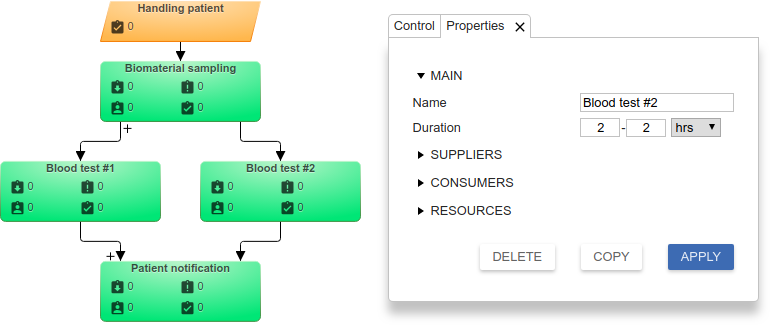
The advantages at the input of the "Patient notification" function mean that the function should wait for the results of both analyzes, and not send a new notification each time with the result. Learn more about the Rule distribution of tasks from suppliers.
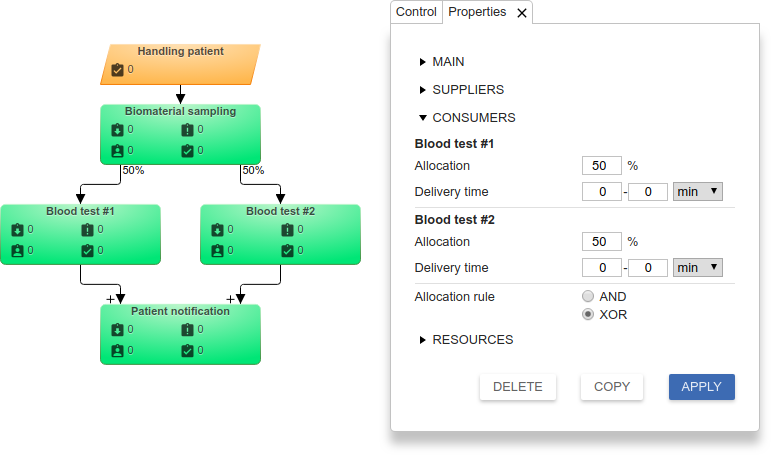
Version #2: 1 client and 2 excluding parallel tasks
Now consider an example where the patient needs to do not two analyzes, but only one of them. Let's change the Rule distribution of tasks to consumer of the "Biomaterial sampling" function on OR with a 50% probability. This means that the patient with the same probability will be made either by Analysis No.1 or Analysis No.2.
Version #3: 1 client and 2 non-exclusive parallel tasks
And how to simulate the option, when the doctor can prescribe analyzes # 1 and # 2 with independent probability relative to each other? This distribution rule is called non-exclusive OR and is not implemented by the service functionality. But you can implement the OR gate with a combination of XOR rules and an additional model object, as shown in the following figure.
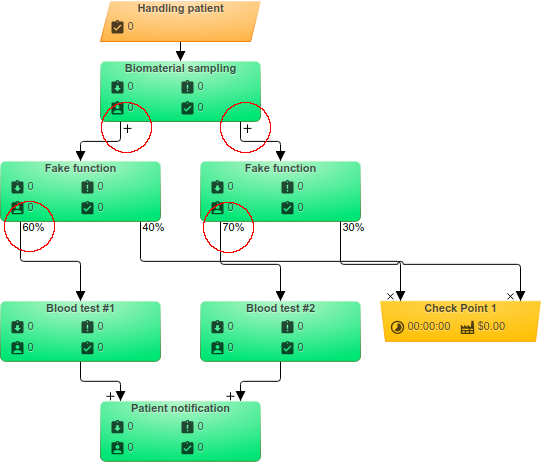
Here, as an unused route recipient, an object of the Checkpoint type is used, but any of the objects involved in routing, for example an Event can be applied.
Version #4: compliance with EPC notation
Let's bring this model, corrected for simulation, to the notation of EPC business process modeling. For this you need to add:
- Events that start or end each function
- Input information or document required to perform the function
- Output or document resulting from the function
- Position or role of Executive function
- Resource - material, information system, which are expended on the performance of the function